Interface BMP280 Sensor With Arduino
The BMP280 is a widely used sensor that measures temperature, barometric pressure, and altitude. Today we are going to learn to interface the BMEP280 Sensor with Arduino. It gives your Arduino project the ability to sense the environment with a BMP280 sensor.
The BMP280 sensor is relatively simple to use. It is pre-calibrated and you don’t require any extra components. So you can start measuring temperature, barometric pressure, & approx. altitude using Arduino and BMP280 sensor.
Components Required
The following are the lists of the components that are required for Interface BMP280 Sensor with Arduino.
| S.N | Components Name | Description | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arduino UNO | ARDUINO UNO R3 | 1 | https://amzn.to/2L0iZf2 |
| 2 | BMP280 | Barometric Pressure & Altitude Sensor | 1 | https://amzn.to/2OmfYav |
| 3 | Jumper Wires | Male to Male Jumper Wires | 4 | https://amzn.to/2JWSR44 |
| 4 | USB 2.0 cable | USB 2.0 cable type A/B | 1 | https://amzn.to/3688OwF |
Introduction to BMP280 Sensor
The BMP280 sensor contains Bosch’s next-generation digital temperature and pressure sensor. It is the successor of the sensors like BMP180 and BMP183.
BMP280 Sensor Measures
As I already mentioned above, The BMP280 is a three in one Environmental digital sensor that measures:
- Temperature
- Barometric pressure
- Altitude
Accuracy and Operation Range of BMP280 Sensor
The following table shows the Accuracy and operation range of the temperature, pressure, and altitude of the BMP280 Sensor:
| Sensor | Accuracy | Operation Range |
| Temperature | +/- 1.0ºC | -40 to 85 ºC |
| Pressure | +/- 1 hPa | 300 to 1100 hPa |
| Altitude | +/- 1 M | 0 – 30,000ft |
BMP280 sensor specifications
- Power Requirement 3.3V or 5V (Module comes with built-in LM6206 3.3V regulator)
- Easy to interface with any microcontroller.
- The BMP280 consumes less than 1mA during measurements.
- The module features Both I2C and SPI communication protocol. So, it can be easily interfaced with any microcontroller of your choice.
- We can change the default I2C address of the BMP280 module with the solder jumper beside the chip.
BMP280 Sensor Pinout
The following table is the BMP280 sensor Pinout table:
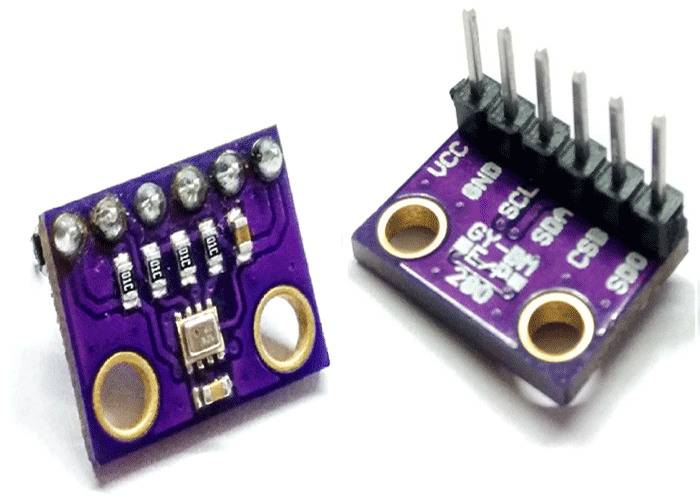
| VCC | Powers the sensor |
| GND | Ground Pin |
| SCL | SCL pin for I2C communicationSCK pin for SPI communication |
| SDA | SDA pin for I2C communicationSDI (MOSI) pin for SPI communication |
| SDO | SDO (MISO) pin for SPI communication |
| CSB | Chip select pin for SPI communication |
Interface BMP280 Sensor with Arduino UNO
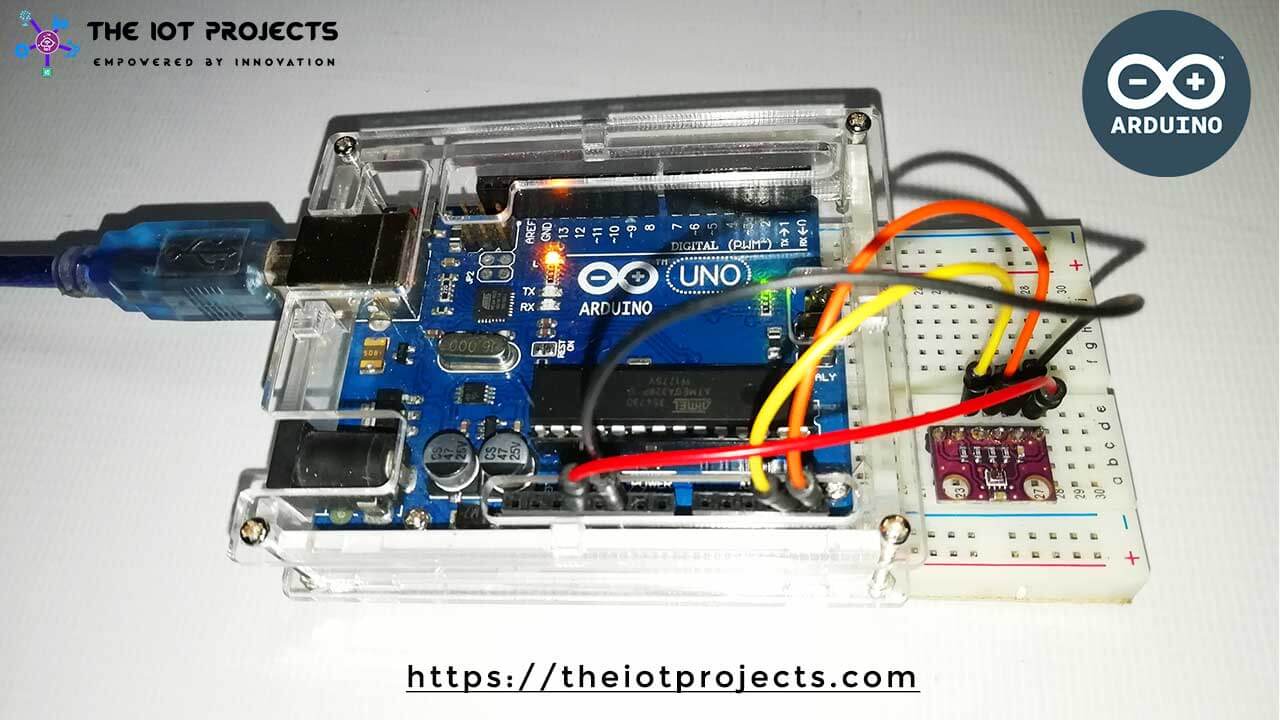
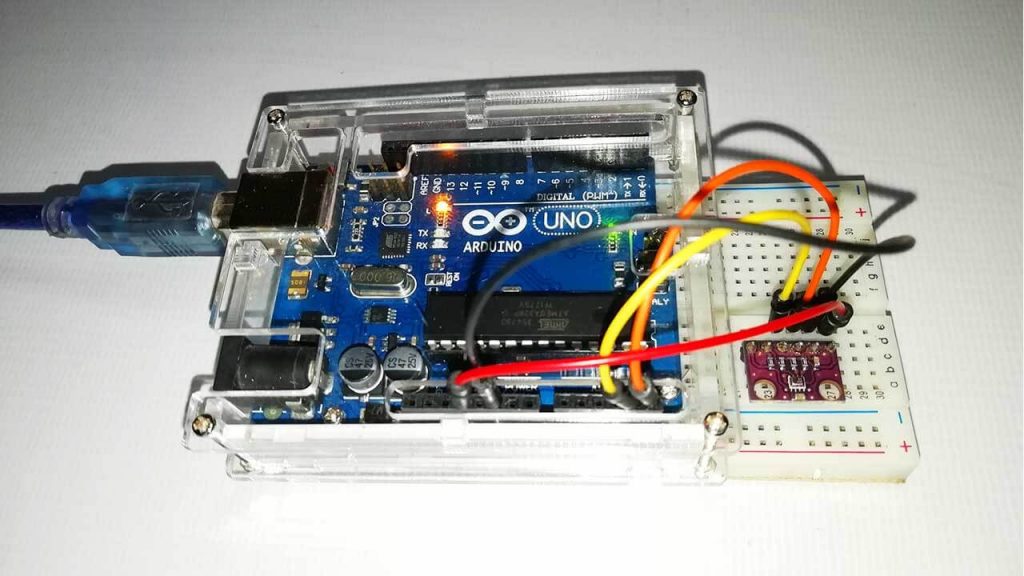
Now, Let’s wire the BMP280 sensor with the Arduino. The Connections are fairly simple. Start by connecting the VIN pin to the 3.3V output on the Arduino and connect GND to the Ground Pin.
We use now the remaining SCL and SDA pins for I2C communication. Connect the SCL pin to A5 and the SDA pin to the A4 pin of Arduino, respectively.
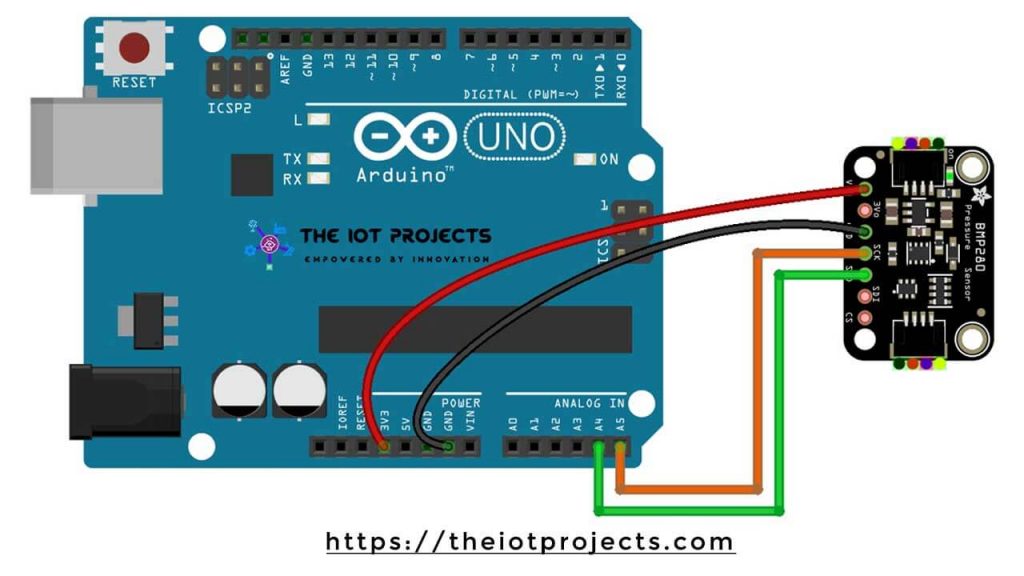
| BMP280 | ARDUINO UNO |
| Vin | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SCL | A5 |
| SDA | A4 |
Recommended Readings:
- Simple Weather station using Arduino & BME280 Barometric Pressure Sensor
- BME280 Based Mini Weather Station using ESP8266/ESP32
- Interface DHT11 Sensor with Arduino and LCD
- Interfacing BME280 Sensor With Arduino
Programming Code
To program the BMP280 sensor with Arduino, we need the following libraries.
These two libraries make our program simple. We can just use a simple command to read the temperature, barometric pressure data, and approx. Altitude data.
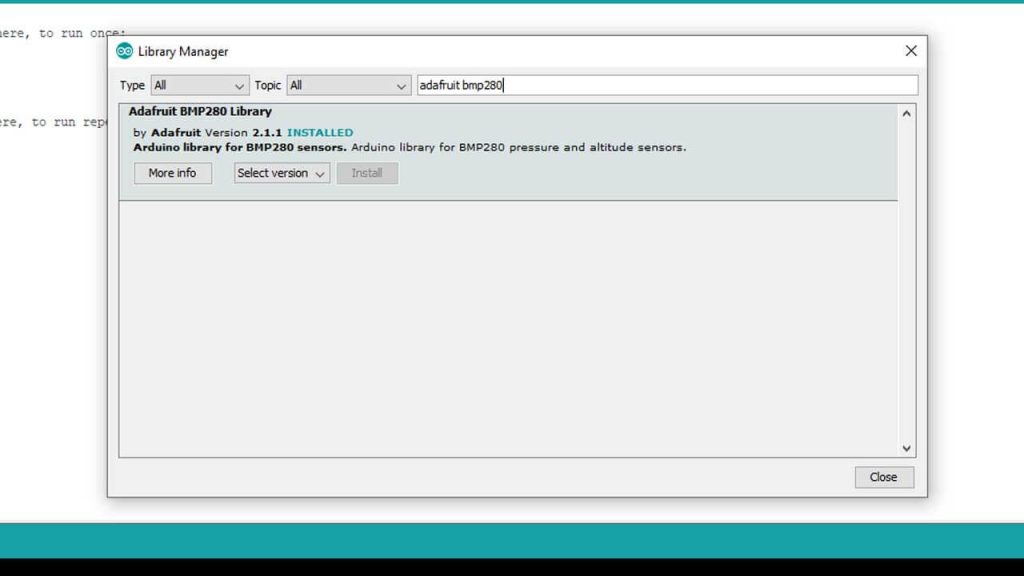
Installing Adafruit BMP280 and Adafruit Unified Sensor Library
To install the library, navigate to the Sketch > Include Library > Manage Libraries… Wait some time for Arduino IDE to update the list of installed libraries.
Now in the search field search for “Adafruit BMP280” and install the library as shown in the image below.
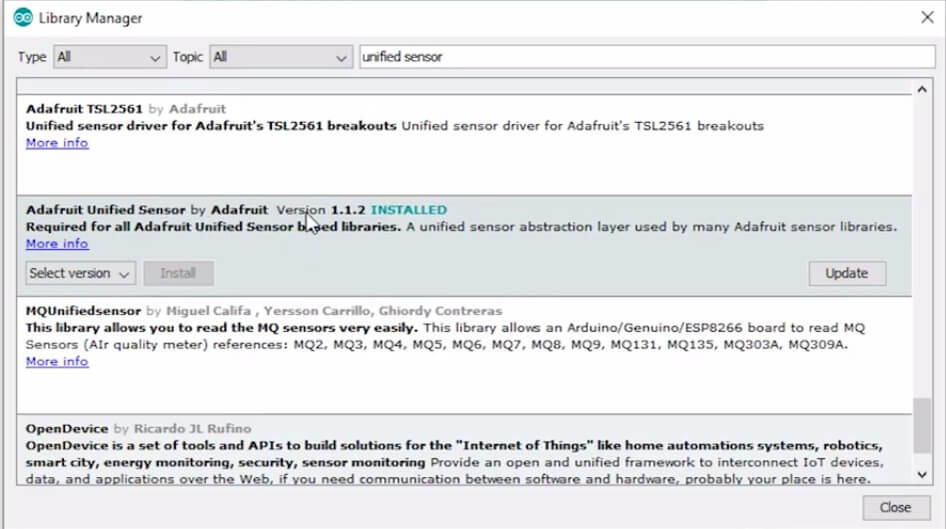
Again, search for “Adafruit Unified Sensor” and install that library as well.
Check the Default I2C address for BMP280 Sensor
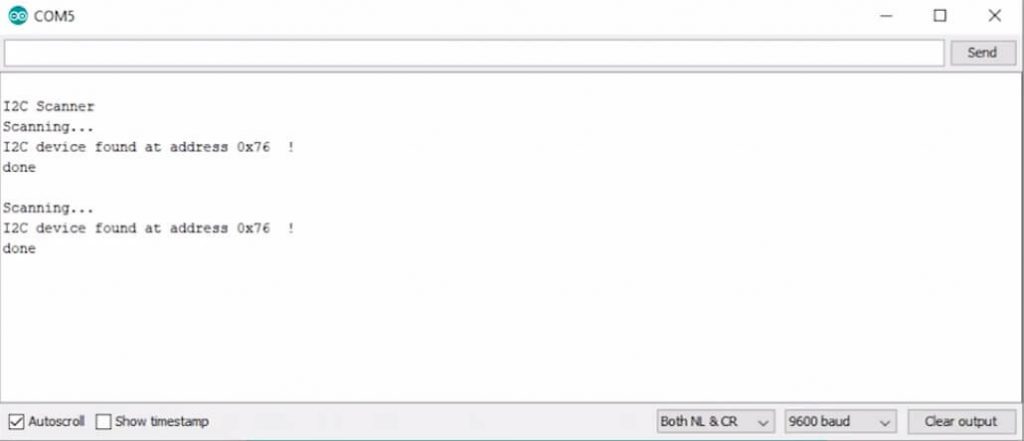
To check the default I2C address of your BMP280 sensor with Arduino. Simply upload the I2C Address Scanner code below. Now, open the serial monitor to check your BMP280 default I2C address. This code will also help you check your sensor working or not.
// I2C address Scanner code
#include <wire.h>
void setup()
{
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial); // wait for serial monitor
Serial.println("I2C Scanner");
}
void loop()
{
byte error, address;
int nDevices;
Serial.println("Scanning…");
nDevices = 0;
for (address = 1; address < 127; address++ )
{
// The i2c_scanner uses the return value of
// the Write.endTransmisstion to see if
// a device did acknowledge to the address.
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0) { Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x"); if (address < 16) Serial.print("0"); Serial.print(address, HEX); Serial.println(" !"); nDevices++; } else if (error == 4) { Serial.print("Unknown error at address 0x"); if (address < 16) Serial.print("0"); Serial.println(address, HEX); }
}
if (nDevices == 0)
Serial.println("No I2C devices found");
else
Serial.println("done");
delay(5000); // wait 5 seconds for next scan
}
Now copy the example program code of the BMP280 sensor from below.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_BME280.h>
define BMP_SCK (13)
define BMP_MISO (12)
define BMP_MOSI (11)
define BMP_CS (10)
Adafruit_BMP280 bmp; // I2C
//Adafruit_BMP280 bmp(BMP_CS); // hardware SPI
//Adafruit_BMP280 bmp(BMP_CS, BMP_MOSI, BMP_MISO, BMP_SCK);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(F("BMP280 test"));
if (!bmp.begin()) {
Serial.println(F("Could not find a valid BMP280 sensor, check wiring!"));
while (1);
}
/* Default settings from datasheet. / bmp.setSampling(Adafruit_BMP280::MODE_NORMAL, / Operating Mode. / Adafruit_BMP280::SAMPLING_X2, / Temp. oversampling / Adafruit_BMP280::SAMPLING_X16, / Pressure oversampling / Adafruit_BMP280::FILTER_X16, / Filtering. / Adafruit_BMP280::STANDBY_MS_500); / Standby time. */
}
void loop() {
Serial.print(F("Temperature = "));
Serial.print(bmp.readTemperature());
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print(F("Pressure = "));
Serial.print(bmp.readPressure());
Serial.println(" Pa");
Serial.print(F("Approx altitude = ")); Serial.print(bmp.readAltitude(1013.25)); /* Adjusted to local forecast! */
Serial.println(" m");
Serial.println();
delay(2000);
}Then upload the code to the Arduino. Now open the serial monitor. You can see the BMP280 Sensor test is running. If you see the error message like: “Could not find a valid BMP280 sensor, check wiring” then you need to change your BMP280 default I2C address in the Adafruit_BMP280.h file.
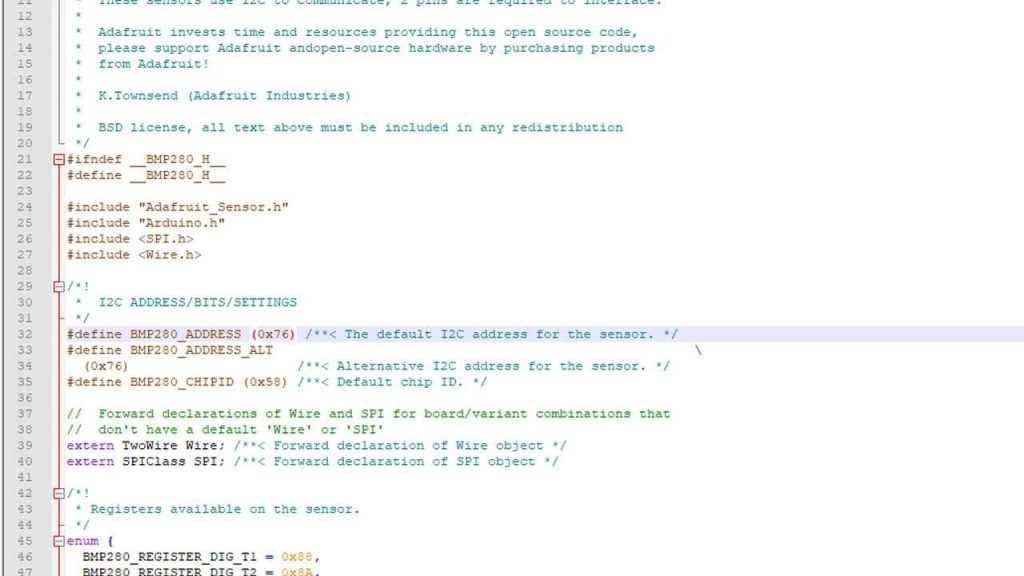
The Adafruit_BMP280.h file located at: DocumentsArduinolibrariesAdafruit_BMP280_Library. For reference, check the image below.
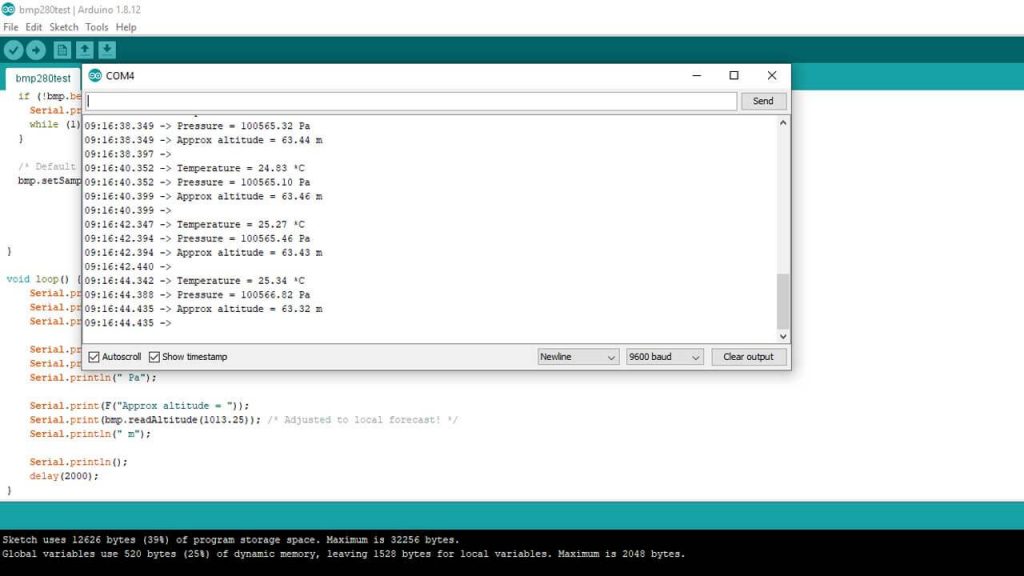
Now, re-upload the code and check your Serial Monitor. Finally, you got the temperature, barometric pressure data, and approx. Altitude data from the BMP280 sensor using Arduino IDE.
BMP280 with Arduino Video Tutorial
Conclusion
So, that’s all for Interface BMP280 Sensor with Arduino. I hope you found the tutorial useful. Now, which project do you like to see using the BMP280 sensor module? Let me know in the comments below.